Why is consumption of fish recommended?
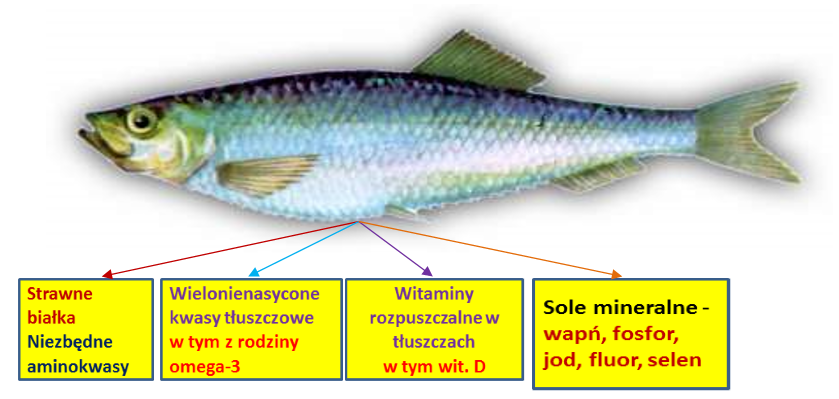
| Digestible proteins Necessary amino acids |
Polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the omega-3 family | Vitamins soluble in fats, including vitamin D | Mineral salts – calcium, phosphorus, iodine, fluorine, selenium |
Fish and processed fish provide valuable nutrients:
- easily assimilated proteins, with the digestibility of over 90%
- necessary amino acids with a beneficial composition, which allows the body an optimum use of proteins,
- vitamins soluble in fats, especially vitamin D3, which is responsible for calcium and phosphorus metabolism and regulates the insulin level by affecting the blood sugar level,
- macro- and microelements – calcium, phosphorus, fluorine and especially iodine and selenium. Iodine deficiencies may cause enlargement of the thyroid gland while selenium deficiencies increase the risk of cancer
But, above all
the necessary unsaturated fatty acids, including the long-chain, polyunsaturated fatty acids form the omega-3 family, including the EPA and DHA acids, which do not occur in other food products.
According to the American and European scientists, the beneficial impact on our health of these acids:
- helps avoid heart diseases and hypertension,
- decreases the mortality of patients with coronary heart disease,
- reduce the tendency for increased blood clotting,
- is antiatherosclerotic,
- is beneficial to the work of brain,
- decreases the risk of cancer,
- improves your general condition,
- is beneficial to your immune system,
- decreases the blood triglycerides level.
1. EPA + DHA in the fish muscle tissue and processed fish
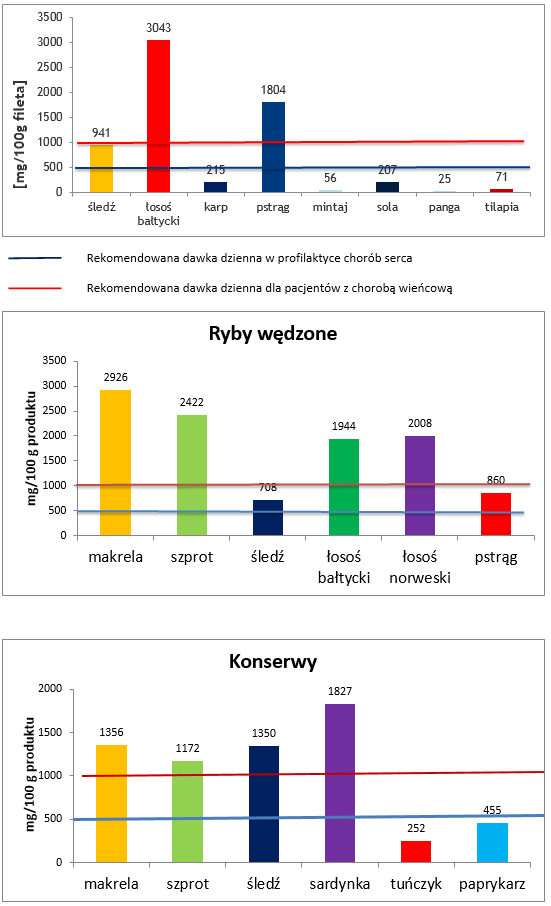
EPA+DHA
[mg/100g of fillet]
herring, Baltic salmon, carp, trout, pollock, sole, pangasius, tilapia
Recommended daily dosage in heart diseases prevention
Recommended daily dosage for patients with coronary heart disease
Smoked fish
mg/100g of product
mackerel, sprat, herring, Baltic salmon, Norwegian salmon, trout
Preserves
mg/100g of product
mackerel, sprat, herring, sardine, tuna, paprykarz
2. Average lysine (necessary amino acid) content in chosen species of fish and processed fish
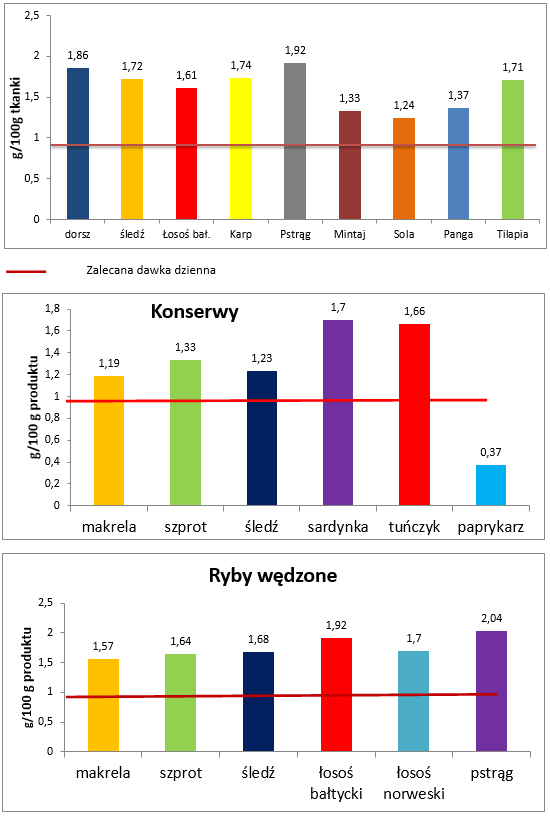
lysine
g/100g of tissue
cod, herring, Baltic salmon, carp, trout, pollock, sole, pangasius, tilapia
Recommended daily dosage
Preserves
mackerel, sprat, herring, sardine, tuna, paprykarz
Smoked fish
mg/100g of product
mackerel, sprat, herring, Baltic salmon, Norwegian salmon, trout
3. Fish, as the main food product which supplies vitamin D3
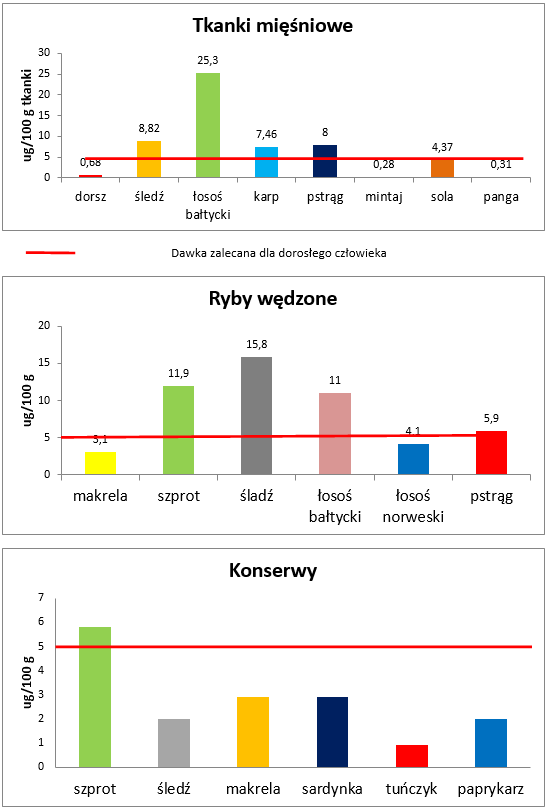
vitamin D
Muscle tissues
µg/100g of tissue
cod, herring, Baltic salmon, carp, trout, pollock, sole, pangasius
Recommended dosage for an adult
Smoked fish
µg/100g
mackerel, sprat, herring, Baltic salmon, Norwegian salmon, trout
Preserves
µg/100g
sprat, herring, mackerel, sardine, tuna, paprykarz
Thanks to their content of n-3 acids, including EPA and DHA, we can classify fish and processed fish as foods with functional properties as they:
– Strengthen the body’s functions by:
- lowering cholesterol levels
- increasing the body’s immunity to inflammations, stress or depression
- their beneficial impact on the development and functioning of the nervous system and brain
– Reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.